Understanding How Parts of a SERP Work to Influence Consumer Perception
Developing creative resources or websites in isolation often leads to the belief that these meticulously crafted assets will be the primary gateway for customers to experience your brand. However, without real-world feedback and engagement, this assumption might not hold true.
In reality, several gatekeepers can stand between your brand and your customer. Even if your brand enjoys high awareness and has a simple URL, an early click or typo will cause a browser to load Google’s SERP (search engine result page). In an instant, your product or service can become but one in a sea of many. SERP is the sum total of all things Google: organic search results, paid ads, map packs, Google Shopping carousels, and tons of other content types and nuances. SERP can either be good to your brand or be a customer’s stepping stone to one of your fiercer competitors.
In today’s Plain Talk article, we’ll discuss some of the ways you can tame the three parts of a SERP to your brand’s advantage.
- Don’t Overlook Any Approach to Ranking
- Be Mindful of How Your Brand Appears in the Different Parts of a SERP
- The Future of SERP
- Get Expert Help Understanding the Parts of a SERP
Don’t Overlook Any Approach to Ranking
We have certainly seen our fair share of brands who have invested heavily in specific areas of SERP, like search engine optimization or paid search, while neglecting an essential practice like reputation management. In other situations, investment in organic search will be prioritized, while paid search or review management is deemphasized despite typically being located closer to the top of SERP. The truth is that none of these three approaches can be ignored.
Neglected reputation management can undermine your SEO and paid search efforts. Questionable or inconsistent reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, Crunchbase, and industry-specific sites will stymie your hard work and investment. Perhaps most critically, brands with a 2.7 or 3.5 Google rating will rarely appear in the first five results in a map pack—always toward the top of SERP and increasingly the primary building block of consumer consideration sets. This “miss” will almost ensure that a potential customer will never reach your conversion-optimized (and likely very expensive) website.

Be Mindful of How Your Brand Appears in the Different Parts of a SERP
This means that brands must be mindful of how they appear in paid search, map packs, and organic results. These all work in concert to influence consumer perception prior to their movement to an owned digital environment like a brand website. SERP, not your brand’s website, is going to be the context in which most people interact with your brand for the first time.
This fact highlights a clear imperative as marketers continue to plan for Q1 and beyond. Invest equally in the three competencies that drive SERP dominance—paid search, reputation management, and organic search optimization.
Now more than ever, it is critical to choose a marketing partner that understands the interplay between these three competencies so that your marketing spend and conversion funnel—perhaps more susceptible than ever to competitive presence and influence on SERP—remain as efficient and competitive as possible.
The Future of SERP
It doesn’t take a fortune teller to know that Google moves the goal post on search with some frequency. That won’t change. Brands can count on changes to SERP to occur at any time. These changes will be driven by two key factors:
- Providing Google’s users with a specific and accurate answer to their query as soon as possible (and more often than not, without requiring a click away from SERP)
- Driving additional revenue for Google
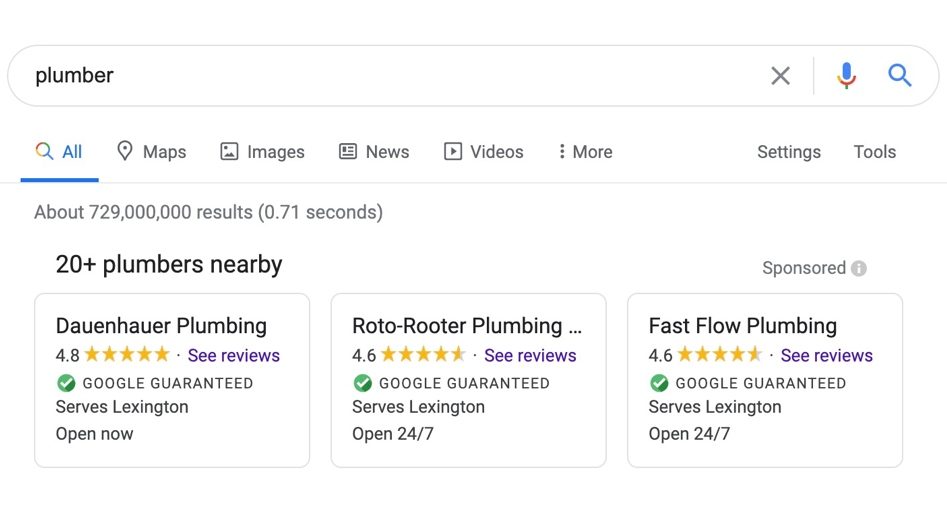
A recent example of a critical SERP change is Google’s Local Services Ads service, which allows advertisers in select industries to appear at the very top of SERP—even above paid search text ads. This carousel-style pack prominently displays the name of the firm, five-star rating scale, service area, hours of operation, and often a Google Guarantee as a badge. This signifier indicates that Google will reimburse customers who reach out to a business through Local Search Ads in the event they are not satisfied with the quality of work (up to a lifetime maximum of $2,000).
This paid carousel makes it incredibly easy to connect users to the information they are looking for—a plumber in the example below – while driving paid advertising revenue for Google. It’s a win-win.
In addition to new products and user experience engineering, factors outside of Google can also influence SERPs. An antitrust lawsuit filed against Google by the United States Department of Justice in late October 2020 may result in new changes to SERPs that deemphasize paid tactics.
Get Expert Help Understanding the Parts of a SERP
While managing your brand SERP can be a moving target, we believe for the near term, that by focusing on organic search, paid search, and reputation management, you will have the best opportunity to shine through in search results, ensure a smooth customer journey, and convert more users.
We’re constantly monitoring changes in search that will impact your business. If you have any questions or would like to learn more from the digital strategy team, please give us a call at 502-499-4209 or contact us here.
Our Articles Delivered
Signup to receive our latest articles right in your inbox.