This year at Google’s I/O 2023 conference, Google unveiled a host of new products and features, and unsurprisingly, the focus was on efforts and advancements made by leveraging artificial intelligence (or “AI”). It was so important to Google to establish expertise, authority and trust (sound familiar?) in all things AI that Google execs used the phrase “AI” more than 100 times during the 2-hour keynote. In this edition of Plain Talk, we’ll discuss what we know (and what we don’t) about the future of artificial intelligence in search and what you can do now to ensure you are capturing low-hanging fruit. We’ll look at:
- The year of the robot – a year full of AI landmarks
- AI’s role in search in the past
- Things you should know about generative AI in search
- Tips to prepare for generative AI
The year of the robot
AI has been a trending topic this year thanks to major advancements in generative AI and large-language modeling (LLM) technology. One of the most notable announcements happened in November 2022 when OpenAI rolled out ChatGPT. This conversational generative AI chatbot uses natural language processing to understand and deliver responses to requests for information, the development of new content, or assistance with specific digital actions like writing code. It works very similar to any search query you’ve ever entered into a search engine (like Bing or Google) – you type in a topic or question, and the “machine” processes all of the data it can access (trillions of data points) and provides you with relevant results or information within seconds. The difference is that ChatGPT (or any generative AI chatbot) doesn’t just spit out a list of relevant links and wish you luck; rather, it generates a new output that combines the various data points into cohesive copy, all with the click of a button. It also remembers and learns as it goes, making the entire experience feel conversational and efficient. It’s not perfect, but it’s easy to see how this innovation will completely change how people obtain information and use the internet. Why would you ever search in a “normal” search engine again?
Thus began a proverbial “race to the moon” as search giants vie to become crowned champions of AI, with a focus on advancements in AI language processing that will revolutionize the search experience specifically. In February 2023, Microsoft announced a reinvented search experience with the updated AI-powered Bing search engine in the Edge browser. Google (who seems to be one step behind at every turn) rolled out Bard, their conversational generative AI chatbot competitor, in March 2023, and in May 2023, they announced their AI-powered “Search Generative Experience” in Google Search Labs through the Chrome browser or Google app.
With tech giants focusing on the “search of tomorrow,” many marketers and business owners are wondering how this will impact their business and bottom line. The fact is, for many businesses, search engine results (SERP; both organic results and paid listings) are the top relevant traffic drivers to their websites and stores, typically generating the highest return on marketing spend. That’s because the act of searching for information signals interest and intent, giving companies the opportunity to reach potential prospects who have an immediate interest and need in your product or service. While Bing was first to market with a generative AI-fueled search experience, Chrome still holds the lion’s share of web browsing (particularly on desktop), and Google is the most used search engine in the world. So, when Google does something, people take notice, and when multiple search engines and browsers are incorporating generative AI to reimagine the search game, marketers and business leaders need to pay attention.
A quick look back: search through the years
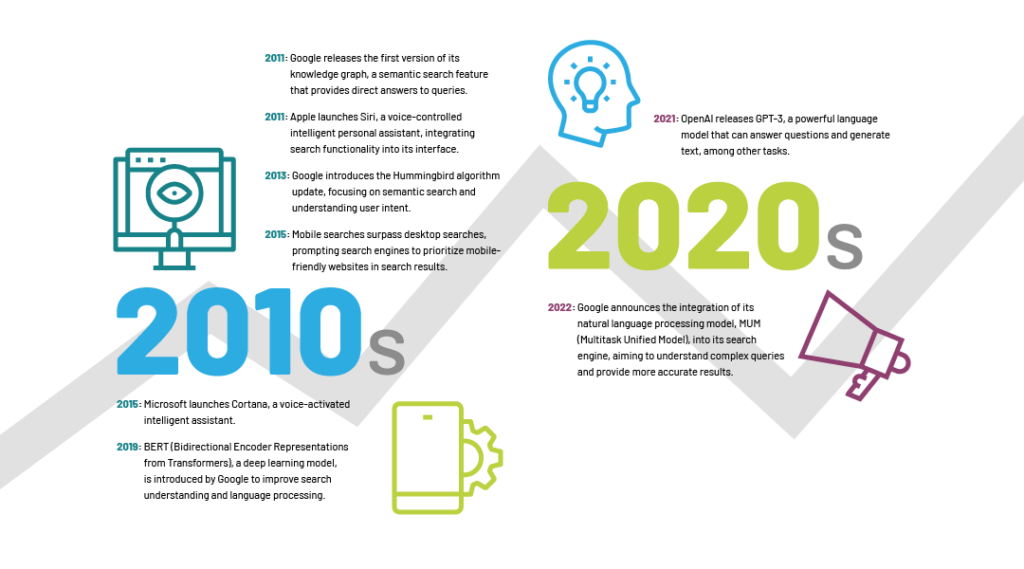
To be 100% clear – this is not the first time AI has been used in search. All search engines use AI algorithms to understand intent, decipher natural (human) language, and deliver relevant and useful results. The idea of using a computer to find and retrieve information began in the 60s and quickly evolved, but it wasn’t until the early 2000s that AI was introduced. Google’s AI efforts began in 2015 with RankBrain, which was said to help the machine understand how words and concepts were interrelated – the machine could understand the intent and context of the query, not just the words themselves. Google continued to evolve the behind-the-scenes AI algorithms so that the results were more relevant, useful, accurate and personalized. Still, it never really looked or acted that different until this year. Generative AI differs from predictive AI because it can actually create something new with the information and inputs provided.
Three things you should know about generative AI in search
So, now that we know where search has been, let’s look forward to what it may become.
1. Generative AI search is new and evolving – and you can shape the future
Generative AI used for search queries is really new, and it’s going to continue to evolve fast. The natural language models are still learning – ChatGPT, for example, doesn’t have a lot of rich data prior to 2021. The “I” in AI stands for intelligence, which indicates that a machine can think like a human and can learn over time. This means there will be mistakes and misinformation provided … but it also means it will adjust, and we have the perfect opportunity to help raise it and nurture its growth – training it to make sure it has the right information.
When we searched on Chat GPT for advertising agencies in Louisville, KY, it gave me a list of 4 local agencies, and we were not listed. I asked ChatGPT a follow-up question: “What about PriceWeber?”. The polite AI chatbot apologized for the oversight and provided the same information about PriceWeber. Later, I went back and started a new chat, this time asking, “What are the best ad agencies in Louisville?” The results were similar, but this time PriceWeber was on the list. Google’s Search Generative Experience hasn’t been as quick to adjust the results in our home tests, but the impact should be the same – if you continue to tell the machine when it leaves out or misrepresents important information, it will adjust and learn. And really, who better to teach it about your business than the people who know it best?
2. SEO is the secret to being one of the “chosen”
With generative AI powering search, when a user enters a search query, the Google machine (or Bing if you roll that way) deciphers, based on all of the historical and current data available, what that person is looking for and then it combs through all of the available data sources (i.e., websites) to craft an extremely specific, detailed and relevant answer. All of this happens right before your eyes, in milliseconds. How do you think the algorithm decides which articles to pull from? You guessed it – high-ranking, high-authority pages with trustworthy and useful content will win here. Your #1 goal right now should be continuing to feed the machine with the right signals that make your business information stick out (positively). What areas within SEO will have the greatest impact?
a. Overall business presence – This includes Map Packs, Google Business Profiles, reviews and overall ranking. When you ask AI to curate a list of “best” or “top” companies, brands, or products, it’s going to look at the data it has – specifically what other people are saying about your company in the form of reviews. It will also pull specific information your company provides to Google, like where you are located, sales and promos, expertise, size of the company, years in business, etc.
b. Rankings, authority and content – Google released a PDF overview of Search Generative Experience (SGE) that, unfortunately, does not hold all of the secrets to their algorithm but does point to some information about how it generates its responses. According to Google, SGE “has been purposefully trained to carry out tasks specific to search, including identifying high-quality web results that corroborate the information presented in the output. These models are used in tandem with our core ranking systems to deliver helpful and reliable results.” Since SGE is still used in conjunction with Google’s core ranking system, that means while high-ranked results will typically float to the top, authority (established with quality content, popularity and proper backlinking) and helpfulness/usefulness of the content based on the intent of the search (completeness of information including various perspectives – like risks and benefits, pros and cons, etc.) can benefit even lower-ranking pages.
c. SEO approach – Just as voice and image search capabilities required us to adapt our SEO strategy, long-tail conversational queries will require us to adjust our approach to keywords and rankings. Battle mapping (looking at all the potential avenues and planning out your true priorities or best opportunities for success with your customers) will allow you to focus SEO efforts on the most important pieces of your business. Organic traffic to your site may decrease as generative search evolves, but you still want to be visible in as many relevant searches as possible, which will not only help your SEO efforts but will also cement your expertise in the minds of searchers.
3. It’s a pay-to-play world, and search ads are not going away
Some people are concerned about the future of search engine marketing with the use of generative AI chatbots. Why would anyone continue clicking on ads or visiting websites one by one when they can get all the information they need in one place? With over half of Google’s revenue coming from paid advertising, we promise you that Google will not let search ads die. There’s too much at stake (like $224 billion), and there’s no such thing as a free lunch. The search space is already pay-to-play with sponsored ads taking up the majority of the first scroll – sponsored local services ads, shopping ads and even sponsored map ads at the top of the organic listings – you have to spend money in order to indeed be in the top results positions. The goal is to drive relevant traffic to your site and get some conversions, whatever those look like for your business, and in order to do that, you have to put some money behind your efforts to help boost your presence and popularity both organically and in paid positions.
We don’t really know what paid advertising will look like in Google SGE – the ad slots may look different, but it will still be pay-to-play, and it may become even more competitive than it is now as brands and businesses compete for the coveted spots within the chatbot. Google is supposedly testing this, though, in our own test queries, we haven’t received ads on SGE. We have received shopping ads on AI-powered Bing via Microsoft Edge, which they rolled out in March. These ads were somewhat relevant but didn’t match the intent of some of our chat queries. So, what does generative AI mean for paid search? Here are some areas to watch:
a. Get ready for increased cost-per-clicks (CPCs) and lower click-through rates (CTRs) – Advertising space is real estate for your messaging, and it’s all about supply and demand. With less supply (search result slots) and greater demand (businesses wanting to get in front of their consumer), the competition heats up, and prices Add that to the very real concern that the generative AI bot can negate the need for people to “click” for more information. It will become harder to get engagement and more difficult to drive traffic to your content or page, which would technically impact your ad rank score, making it more difficult to “win” in the auction space without spending more. (Whew, that was a spiral.)
b. Get ready for lack of control – it’s evident from our experience that Google has been slowly prepping us for this over the past 12 months. If you manage search campaigns, you know that Google has been pushing for more automation and, ultimately, less control. The optimization score provided by Google (an estimate of your campaign’s potential) is focusing more and more on three things – budget (weird how they never recommend you spend less), dynamically created assets (keywords, images, headlines, etc. either pulled from or developed using information pulled from your website), and less targeting specificity (they want the algorithm to “do the work” so are pushing more general “broad match” keywords and fewer guardrails on where the campaigns run or whom they reach).
Three tips for things you can do now to prepare for generative AI:
1. Focus on incorporating and leveraging strong “action” ad types for conversions – Call ads, shopping ads, and local service ads. All of these have an immediate action associated without having to go to a landing page. These ad units already provide some of our best performance metrics to date because they offer a direct connection to someone ready to take action, whether that’s a phone call, a message to a Google-verified professional or a “buy online” purchase.
2. Start using 1st party data and enhanced conversions – Providing Google (or Bing) with information about your customers (whether they converted online or offline) will help inform the system about additional engagement and traffic. This will not only let you optimize against that data but may also help improve engagement signals that impact ad rank.
3. Start experimenting now. If you haven’t tested Performance Max campaigns, you probably should. With these campaigns, you tell the Google machine what your goal is, you provide assets (images, videos, headlines, descriptions, etc.), and you let Google decide where to run your ad based on the keywords and search queries you are targeting and what combination of assets to use to generate the best results. The ads can run on YouTube, Google Maps (if you use the location extension), Gmail, or a shopping carousel. You have no control over the final combination served or where the ad runs, but you do control the budget and the assets used (unless you use dynamic assets, in which case Google will do what it wants). Testing with even a small budget now will help you learn how to maximize the limited inputs so that you meet your goals.
Better results are coming (eventually)
Get ready for better results, eventually. The best part about AI is that it’s a tool that can help accomplish a specific thing efficiently and often effectively. While CTRs may decrease, you can still achieve your goals and meet your KPIs if you use the tool correctly.
Generative AI used for search aims to improve everything about the search experience, and it will measure that improvement based on results – to get better results. It will learn and evolve along the way, which will end up benefitting users, marketers and businesses with its powerful targeting capabilities, efficient and data-driven ad copy development and automation of repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. This will provide marketers with the enhanced ability to adapt and remain nimble and to focus on the to-dos that will provide the most value.
The takeaway:
We are on the precipice of major evolution in search – it will never be the same. While this is exciting as a user, it may be a little nerve-wracking for the marketer who must deliver results by giving up control of “the machine.” However, you have to admit that a refined search experience for the user combined with the automation and effectiveness of AI sounds promising. With the certainty of these changes, now is the time to experiment and develop expertise (or partners with expertise). If you have questions about how to prepare your business for AI search, drop us a note or call us at 502-499-4209. Like what you read today? If you’re not already a subscriber to our Plain Talk newsletter, you can subscribe below.